
Christiane Taubira the former French minister of justice likes to remind the public of the government’s responsibility toward the vulnerable. She had to defend this position while trying to make the penal system in France more comprehensive. She was only partially successful. The state of vulnerability comes very fast when unwanted pregnancy starts. Even though such situations are produced by a man and a woman, the burden remains entirely on the woman. If we add another layer to the state of vulnerability, such as poverty, things become immediately more complicated for the woman.
In the United States, the state does not assume its responsibility toward the vulnerable, who are sexualized, racialized and declassified instead of being supported. The state uses the vulnerable as a source of surplus value through its imprisonment making the institution an industrial complex with contractors running the game. They even charge women prisoners for their basic amenities, such as soap. In this combination of neoliberal development of consumerism and unfettered capital gain, punishing women as members of the vulnerable combines growing inequalities with awesome wealth building.
Trump and his team have brought this idea to its paroxysm, but everything was in place before this election.
The right to abort is a constitutional right that should be respected everywhere, but the case of access to abortion points to the lack of reproductive justice, inside prison and outside. Women in need of abortion often experience stigmatization, reinforcing the sentiment of disqualification as full citizens. In prison, the challenge to wield this right to abortion is real, with enormous discrepancies from state to state and from county to county.
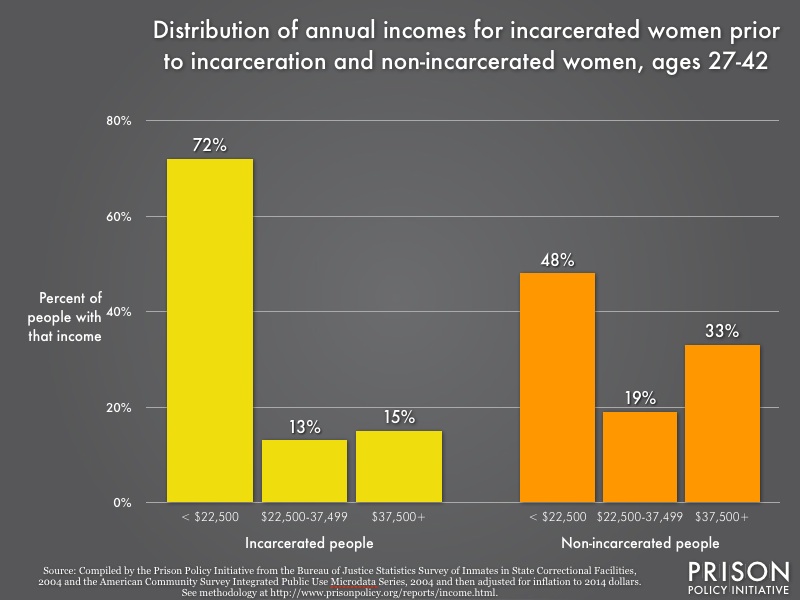
Worldwide, 33% of women prisoners are in the US, and so it is important to examine the reasons for the push to punish women with the detention conditions worsening the punishment itself. The number of incarcerated women in the United States has increased 700% between 1980 and 2014. Being poor is a condition for incarceration and particularly affects women. As the Prison Policy Initiative exposed in its latest report 72% of incarcerated women had an income less than $22 500 while the rate is 48% for non-incarcerated women, and for men 23% for non-incarcerated men compared to 57% for incarcerated men.
Pregnant women are sent to prison, jail, or immigration detention centers. In federal prisons 1 in 33 women and 1 in 25 in state prisons are pregnant. The number is hard to establish in other kinds of detention facility.
If women decide or are intimidated to pursue their pregnancy behind bars, they face harsh conditions with disastrous prenatal conditions in detention facilities in general. In 2011, 38 states had no prenatal policies and 41 states did not require prenatal nutrition. Children born in prison are removed from their mothers right after birth, which demonstrates that a child’s well-being has no meaning when the child is born in prison, another double standard.
In addition, there is no adequate health care for inmates in the United States, though, based on the 8th Amendment, prisoners are the only ones who have a constitutional right to medical care. Instead, medical care in prison is often decided through court orders by penal and judicial personnel who have no medical expertise, and so treatments are delayed, ignored, or never performed.
If women inmates don’t want to become mothers, although it is their constitutional right to have access to abortion, few states offer comprehensive solutions. In most of states, the women must deal with a hodgepodge of rules and regulations, all defined from the male-standard of incarceration. Generally, the hurdles are numerous, high, and burdensome. From having access to a clinic to payment to transport, every step is an “undue burden” for women prisoners in most states. As ACLU attorneys recall, the US Supreme Court Roe v Wade decision clearly said “laws that restrict abortion access cannot create an `undue burden.’”
The legal dispute around abortion in prison should be taken seriously by everyone outside of prison who believe that respecting the dignity of women as full citizens means ensuring they control their reproduction. Women have been sentenced to jail for the failure of the state to provide abortion or prenatal services to the vulnerable. The Purvi Patel case is one of too many cases that proves that the State is not concerned with women’s well-being, especially when in a state of vulnerability.
ACLU and other groups have called for more research on the application of reproductive rights inside the United States penal systems. Although this demand is important to resist the conservative anti-abortion wave, the invisibility of living conditions of women behind bars is full of lessons about the way attacks on women’s right and reproductive justice is waged in general and its social meaning. When state leaders are ready to fulfill their responsibilities to serve the vulnerable, often women and more often women of color and/or women prisoners, they will serve all women and the society better.
(Photo Credit: National Women’s Law Center) (Infographic credit: Prison Policy Initiative)