While touting a more progressive and feminist agenda than his predecessor, New Jersey Governor Murphy signed the Diane B. Allen Equal Pay Act, which will expand the protections of the state’s existing wage and hour law and amend the New Jersey Law Against Discrimination to make discrimination in wages on the basis of any protected class an unlawful employment practice. The law should be applauded as a step in the right direction to fix the state’s pay gap disparity. However, New Jersey falls horrifically short when it comes to another women’s issue: maternal health. The maternal health of New Jersey’s women is one of the worst in the country; pregnancy-related deaths, while they are progressively climbing in the United States, is double the national average in the Garden State. Ranking 47thout of 50 in maternal deaths, according to America’s Health Rankings, a report by the United Health Foundations, in New Jersey 37 women die, on average, for every 100,000 live births. The national average is 20.
The disparities for black women in the state are even more grotesque, with African-Americans in New Jersey five times more likely than white women to die from pregnancy related complications. New Jersey’s maternal mortality remains worsethan that of Mississippi(26.5 deaths per 100,000 live births). While New Jersey has one of the lowest infant mortality, the racial gap between Black and White infants is one of the largest in the country. Black babies in New Jersey are three times more likely to die before their first birthday than White babies.
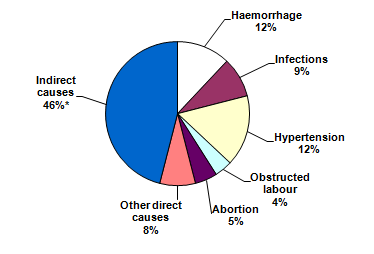
According to a proclamation celebrating the state’s first ever Maternal Health Awareness Day, the leading causes of pregnancy-related death include cardiovascular disease, pregnancy-related heart failure, embolism, septic shock and cerebral hemorrhage. Other factors include obesity, chronic health conditions such as diabetes and hypertension, lack of prenatal care, and drug use.
Members of Murphy’s cabinet have highlighted their concerns about the disparity and have proposed ways to help reduce it. Dr. Shereef Elnahal, the Department of Health Commissioner, and Carole Johnson, Commissioner of the Department of Humans Services, have pledged to improve data collection and modernize government systems to provide more efficient, better quality of care that results in fewer racial disparities in general. They also promised to better coordinate government services to help address housing, transportation, nutrition, and other social factors that have a tremendous impact on the health of vulnerable residents.
Toxic racism, especially in northern New Jersey, plays a significant factor in the inequalities between Black and White women, one that transcends economic or healthcare access. New Jersey only has 15% percent Black population, yet they are the worse off for many of the state’s current health, economic, and criminalization issues. Wealthy, well-educated Black women with quality healthcare experience poorer outcomes than White women, regardless of their economic or social status. Improving the current trends of lack of care for Black women requires greater awareness, but changes in healthcare policy also need to be addressed.
Finally, New Jersey’s Black population is overwhelmingly in poverty, far beyond their White counterparts. The state average rate of poverty is 10.9%. For Whites, it’s 8.3%; for African-Americans the rate is 19.7%. For Black women in New Jersey, poverty is a reproductive rights crisis. Poverty leads to lack of pre-natal care, which contributes directly to one of the highest maternal mortality rates in the United States. New Jersey must address universal access to real healthcare for all. Otherwise, the issue of maternal mortality will continue to besmirch the reputation of the Garden State.
(Infographic Credit: Pix 11)